Description
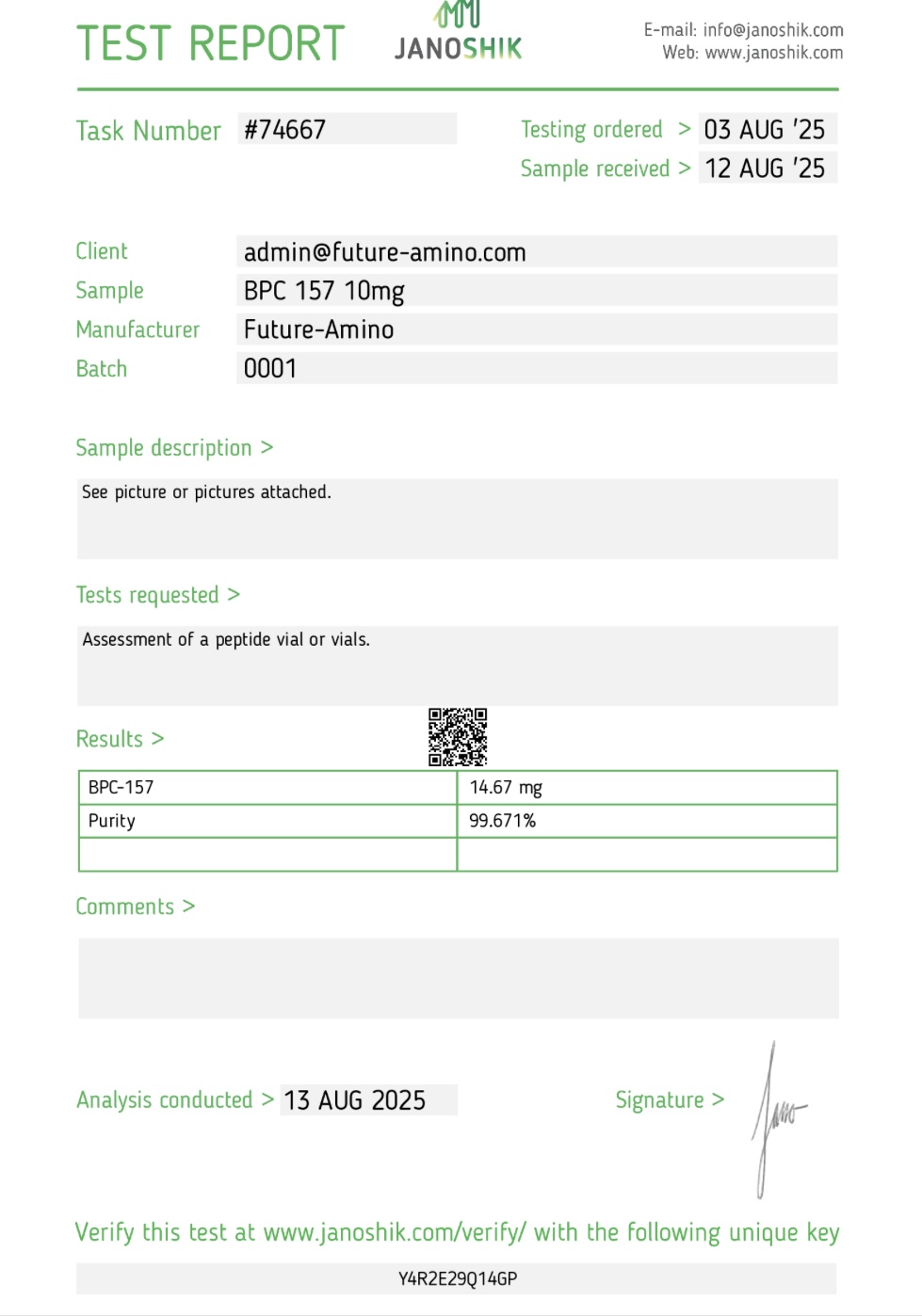
BPC-157 10mg
BPC-157, also known as Body Protection Compound-157, is a synthetic peptide derived from a protein found in the stomach. It has become popular in the UK among athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and individuals recovering from injuries due to its potential benefits in tissue repair, joint health, and inflammation reduction. Research suggests that BPC-157 may help support the healing of muscles, tendons, and ligaments, as well as protect the digestive system and promote overall recovery.Many people search for BPC-157 in the UK as part of an advanced recovery protocol, often alongside TB-500. The combination of BPC-157 and TB-500 is frequently discussed in performance and rehabilitation circles for its potential to accelerate healing and maintain training momentum after injury. BPC-157 may also play a role in improving blood flow to damaged tissues, supporting faster regeneration, and reducing discomfort during the recovery process.
While BPC-157 is not approved as a medicine, it is often researched in laboratory and veterinary contexts for its possible protective and regenerative effects. Users looking for high-quality BPC-157 in the UK should ensure they purchase from a reliable supplier who prioritises purity, accurate dosage, and proper packaging to maintain stability.
Common topics people research around BPC-157 include: optimal dosage protocols, injection techniques, how long to use BPC-157 for best results, and potential synergies with other peptides. In the UK, interest in BPC-157 continues to grow among those seeking a targeted approach to recovery, whether from sports injuries, chronic joint issues, or post-surgical rehabilitation. With careful use and sourcing from trusted providers, BPC-157 is regarded as a potential tool for supporting the body’s natural repair and protection mechanisms.
Bpc-157 Research Insights
Bpc-157 has become an area of growing interest in the research community, particularly because of the way scientists are exploring its potential connections with recovery and adaptation. When discussing Bpc-157 in a research context, most references point toward ongoing investigations in how certain peptides interact with the body. The term Bpc-157 is often mentioned alongside other peptide names in scientific articles, making it part of a larger conversation about experimental compounds and their effects.
In scientific discussions, Bpc-157 has been linked to mechanisms involving tissue and cellular response. While the published research is limited and still developing, there is curiosity about how Bpc-157 might fit into the broader landscape of regenerative studies. Laboratories conducting peptide-related work frequently highlight Bpc-157 in their findings, with emphasis on how it compares to other substances studied in pre-clinical environments.
Historical Context of Bpc-157 Studies
One reason Bpc-157 stands out is the body of preliminary work examining its possible influence on tendons, ligaments, and other connective structures. Some researchers note that Bpc-157 appears repeatedly in journals that catalog peptide research. These references often attempt to clarify how Bpc-157 interacts with natural repair cycles and stress recovery, though the majority of evidence remains early-stage and non-clinical.
In many cases, Bpc-157 is discussed as part of a set of compounds used for investigative purposes only. Because of this, articles tend to emphasize that Bpc-157 is not classified as a medicine or approved treatment. Instead, it remains under review in various forms of animal models and in-vitro testing. Nevertheless, the interest continues to grow as new studies are released.
Comparisons and Related Research
Other compounds frequently appear in the same circles as Bpc-157, such as TB-500 or similar peptides. Comparative discussions help frame Bpc-157 in relation to these other substances. Researchers often note that Bpc-157 has unique properties worth analyzing separately, while also acknowledging that many peptides in this category share overlapping functions or biochemical roles.
When looking at databases that collect experimental research, Bpc-157 consistently ranks among the top entries for queries about peptide-assisted recovery. These data sources demonstrate just how much attention the scientific community is placing on Bpc-157 and related compounds. Even though the results are not conclusive, the sheer number of citations indicates significant academic curiosity.
Limitations of Current Knowledge
Despite all the ongoing discussions, it is important to highlight the limitations. Research on Bpc-157 has not yet reached the stage of widespread clinical application. Most sources emphasize caution, stating that while Bpc-157 is intriguing, its safety, efficacy, and long-term implications are far from fully understood. This is a common theme across peptide studies: an initial burst of interest, followed by years of deeper exploration before any definitive conclusions are made.
Many research teams stress that Bpc-157 must be studied further, particularly in controlled environments where specific endpoints can be measured. As such, the compound remains a topic for specialists rather than something mainstream. Still, the fact that Bpc-157 continues to be listed in new research reports suggests that scientists see enough potential value to continue investing time and resources.
Conclusion
In summary, Bpc-157 occupies a unique space in the peptide research landscape. Its consistent presence in experimental discussions, its role in comparative analyses with other compounds, and the level of curiosity surrounding it all contribute to its reputation as a peptide worth following. Even if its role is still speculative, Bpc-157 provides researchers with another lens through which to explore the possibilities of regenerative science and tissue support.
Bpc-157 Research Background
Bpc-157 continues to be referenced in research discussions as one of the most notable peptides under investigation. The curiosity around Bpc-157 stems from preliminary studies suggesting unique biological activity when observed in controlled conditions. Although the body of evidence is still considered early, Bpc-157 appears in numerous journals and laboratory reports, creating a strong foundation of interest for future exploration.
One aspect that sets Bpc-157 apart is the way it is often included in conversations about cellular repair and recovery. Specialists examining connective tissues, ligaments, and muscle structures have repeatedly noted the potential of Bpc-157 in experimental models. While there is no guarantee that these observations will translate into approved applications, the consistency of Bpc-157 across research papers keeps it in the spotlight.
Bpc-157 in Academic Literature
Researchers often highlight that Bpc-157 has been cited in both in-vitro and in-vivo studies. The compound shows up in animal testing models that are designed to examine repair efficiency and stress adaptation. Even though Bpc-157 has not advanced to the level of licensed medical use, the fact that it is discussed widely in peer-reviewed spaces shows just how strong the interest has become in the scientific world.
In addition, Bpc-157 tends to be compared with other peptides, including TB-500, for its potential involvement in recovery-based processes. These comparative analyses demonstrate that Bpc-157 has distinguishing features worth separating out and exploring further. For example, the way Bpc-157 is referenced in tendon research differs slightly from other peptides, indicating possible unique mechanisms at play.
Experimental Applications of Bpc-157
Many laboratories have described Bpc-157 as an experimental peptide with notable roles in tissue resilience. While the focus is mainly on pre-clinical work, Bpc-157 has carved out its niche in the peptide research ecosystem. Publications have drawn attention to how Bpc-157 may be involved in accelerated repair when observed under specific laboratory conditions, though much more data is required before forming any definitive conclusions.
The conversations surrounding Bpc-157 are typically careful to clarify that no therapeutic claims should be attached to the peptide. Still, the experimental data has been compelling enough to maintain momentum. Year after year, citations of Bpc-157 increase in global databases, reinforcing its reputation as one of the most intriguing topics in peptide science today.
Challenges and Considerations
As with any peptide, there are important limitations to emphasize. The major challenge is that Bpc-157 research remains in its early stages, making it impossible to predict its long-term viability or safety profile. Some researchers are optimistic about Bpc-157’s potential, while others call for more stringent testing and clearer methodologies before drawing solid conclusions. This balance of curiosity and caution is what currently defines the discussion around Bpc-157.
Ethical considerations also play a role in how Bpc-157 is studied. Because the majority of work has been conducted in non-human models, there is a strong push for more rigorous frameworks before human-focused studies can expand. The growing body of references to Bpc-157 in the literature, however, suggests that this process will continue step by step, with each new study adding clarity.
Conclusion
Ultimately, Bpc-157 is a peptide that has earned its place in the ongoing discussions of regenerative and recovery research. While definitive outcomes remain unavailable, the persistence of Bpc-157 in scholarly conversation shows its value as an object of inquiry. For now, Bpc-157 will likely remain a focal point in peptide-related exploration, offering a glimpse into the possibilities of advanced biological support and repair sciences.